Economics 4784: Economic Development
经济学发展代写 Suppose a researcher forecasts that household incomes will fall due to declines in oil revenues that have historically been distributed
This is an open-book style exam. You may consult any resources at your disposal, including your notes, class materials. And a calculator, but you may NOT communicate with anyone during the exam. You may NOT give or receive assistance on this exam. Make sure to write your answer in your own words and demonstrate independent thought. Your answers will be evaluated purely on your typed responses in the text boxes, so be sure to explain your reasoning. No graphs are necessary and images/attachments will not be graded.
There are 10 questions on this exam, including the question which asks you to sign the Honor Code. Aside from the Honor Code question, all questions have equal point value (2 points each). This exam is timed to take 50 minutes and only one attempt is allowed. You will only be allowed to view one question at a time and you will not be allowed to return to questions once you have submitted your response.
Honor Code 经济学发展代写
- This is an open-book style exam. You may consult any resources at your disposal, including your notes, class materials, and a calculator, but you may NOT communicate with anyone during the exam. You may NOT give or receive assistance on this exam. Write your full name below to attest to your compliance with the CU Boulder Honor Code Pledge: “On my honor, as a University of Colorado Boulder student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance.” Type your name.Migration
- Suppose a researcher tells you that, on average, children of international migrants that are left behind in the home country are more likely to attend school compared with children of non
migrants. Provide one causal explanation that could support this correlation between parental migration and children’s outcomes. Provide one NON-causal explanation that could explain this
correlation between parental migration and children’s outcomes. Be sure to label your answers. With reference to your answers, explain why it is difficult to ascertain the causal impact of parental
migration on children left behind.
Answers may vary.
Causal explanation for positive correlation between parental migration and children’s education: Migrant remittances may relax the household budget constraint so children left behind can go to school. 经济学发展代写
Non-causal explanation for positive correlation between parental migration and children’s education: Migration may require positive attributes (e.g. motivation, ability, hidden assets) which are also positively correlated with schooling of children, but these factors may be unobserved to the researcher, making it difficult to control for. Since migrants self-select, these unobserved variables may be causing both the migration and the observed educational outcome.
Land and Labor Markets
- Consider a risk-averse farmer-laborer choosing between 3 contracts: fixed wage, sharecropping, and fixed rent. If output is uncertain and all contracts yield the same expected return to the farmer, how will this farmer rank these contracts (with 1 being the most preferred)? Why? Now consider a risk-averse landowner (non-laborer) choosing between 3 contracts: fixed wage, sharecropping,and fixed rent. If output is uncertain and all contracts yield the same expected return to thelandowner, how will this landowner rank these contracts (with 1 being the most preferred)? Why?
Since all contracts yield the same expected return, the difference between them is based on risk associated with each of them, and both agents are risk averse, so they dislike more risk. Farmer-laborer bears all the risk in fixed rent contract (she is the residual claimant), bears no risk with fixed wage, and shares the risk with landowner under the sharecropping contract.
Landowner bears all the risk in fixed wage (she is the residual claimant), bears no risk with fixed rent, and share the risk with farmer under the sharecropping contract. Farmer-laborer’s rankings: 1 fixed wage, 2 sharecropping, 3 fixed rent. Landowner’s rankings: 1 fixed rent, 2 sharecropping, 3 fixed wage.Rural-Urban
4. You are an economic advisor to the leader of a developing country. Someone suggests that rural to urban migration should be restricted because fewer workers in agricultural areas willnecessarily mean lower output, less food, and lower economic growth. Based on our class discussion, would you agree or disagree with this assessment? Your answer should refer to assumptions regarding the marginal product of labor in agriculture versus industry and the compensation system in agriculture versus industry. 经济学发展代写
Disagree because there may be a surplus of labor in agricultural which could move to urban area and be used in industry, thus propelling industrialization and economic growth without much reduction in output (food), i.e. low opportunity cost, as per the Lewis model.
This would require the marginal product of labor in agricultural to be less than the marginal product of labor of an identical worker in industry (MPL in agriculture approaches 0 in canonical case), which might be the case if agricultural workers are sharing output/yield, as opposed to being paid according to the value of their marginal products of labor, as they are in industry.
Rural-Urban Migration
- There are six sisters who own a small farm in the agricultural sector. The value of their output is 1,200 pesos, which they divide equally. The urban sector has two kinds of jobs. There are
informal jobs, which anybody can get, which pay 100 pesos, and there are formal jobs which pay 400 pesos. The probability of getting these jobs depends on the proportion of jobs in the urban labor force, exactly as in the Harris-Todaro model. You may assume that all sisters are risk neutral.
Assume that one of the sisters, Juanita, compares her own expected returns in the two sectors and that there are no costs of migration. Calculate the threshold probability of informal sector
employment that will make Juanita indifferent between migrating and staying on the farm. If this is in fact the probability of informal sector employment, what is the expected urban wage? Show your work and state explicitly any equations needed to solve this problem.
Wage agro=1200/6=200
Equation needed to solve this problem:
Let p_i=probability of informal job.
100p_i + 400(1-p_i)=200. p_i=2/3
If p_i=2/3, then expected urban wage is 200 pesosRural-Urban Migration
- There are five risk-neutral brothers who own a small farm in the agricultural sector. The full production function on the farm is given below. Number working on farm Total Output (in $)
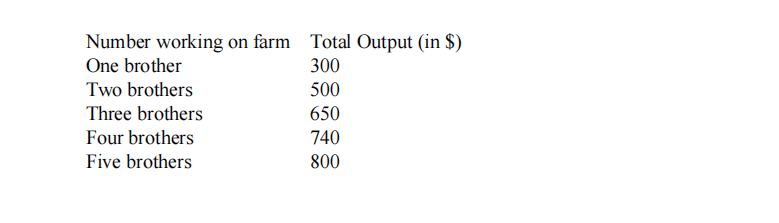
Suppose that the brothers seek to maximize total family income and that the expected urban wage is $100. Assume that there are no migration costs and indifference is resolved be migrating. How many brothers will migrate? What will be the expected value of total family income? Show your work and explain your reasoning.
Value of marginal product of labor on farm for 3rd brother on farm=150>expected urban wage, but 4th brother’s VMPL is only 90<expected urban wage, so 3 brothers will remain on farm and 2 will migrate. Expected family income=650+2*100=850. Population 经济学发展代写
- Suppose a researcher forecasts that household incomes will fall due to declines in oil revenues that have historically been distributed as cash transfers to all families in the area.
Based on our class discussion, what would you expect to happen to fertility rates for these families as a result? You may assume that children are a normal good. Your answer should refer to income and substitution effects and explain how they are expected to operate in this case.
I would expect fertility to fall because non-labor income is falling, so this is a pure income effect (no substitution effect). That means households will consume less of all normal goods, including children.Population
- Suppose policymakers in a country are considering the establishment of a pension program to provide income support for the elderly, but only if they maintain separate households from their children. Give two reasons associated with our class discussion why you would expect this program to lead to a drop in the total fertility rate in this country. Explain.
First reason why fertility should fall: Elderly are not going to be able to provide as much help in raising any grandchildren, since they cannot live with their extended family. This reduces the negative externality which led to overproduction of children when parents were sharing some costs with elderly (grandparents of children).
Second reason why fertility should fall: Pensions will provide income support in old age, reducing the demand for children for that purpose. Parents will not need to have kids to support them in old age if the government will be doing it.
Population 经济学发展代写
- Based on our class discussion and readings, what is the major recent demographic challenge facing both developed and developing countriesthat does not stem from fertility or migration? Why might this pose a particular dilemma in poor countries where leaders would otherwise like to bring down high fertility rates?
Aging of the population is a major challenge for developing and developed countries. It poses dilemmas for poor countries because there are fewer government and private sector support mechanisms to support the elderly as they age (e.g. higher share of informal workers), which means that the elderly must rely on their children for old age support.
So if leaders want to bring down high fertility rates, the question remains: who will take care of the aging population? If people do not see that the government is providing that care, then they will have to keep having lots of children, which means that there will still be a high ratio of dependents to working age people, limiting economic growth.Environment
- Consider the case of an
industry which can emit unconstrained air pollution as part of its production process. What type of market failure is operating here? Based on our classroom
discussion, what could the government do to modify the firm’s polluting behavior? Explain how this relates to the private and socially optimal quantities produced before and after the government
intervention. Be specific. 经济学发展代写
This is a negative externality because the firm can emit pollution, thereby imposing the costs of production on society, so the marginal social costs (MSC) of production are greater than the marginal private costs (MPC) to the firm, the firm overproduces relative to the social optimum (Q_market>Q_socialopt), and there is deadweight loss.
The difference between MSC and MPC is the marginal external/environmental costs (MEC), and the government could impose a tax on the firm equal to the MEC, which would bring MSC and MPC into alignment, i.e., cause firm to internalize externality. This would make the firm produce less, specifically, Q_market=Q_socialopt after the tax, and eliminate the deadweight loss.





发表回复
要发表评论,您必须先登录。