IMM Extra Credit HW(Lorenz system)
常微分方程代考 A key feature of chaotic system is “sensitive dependence on initial conditions”, meaning infifinitessimal difffferences in the initial
This assignment should be completed in a Jupyter Notebook, and turned in as a PDF of the
notebook.
The Lorenz system 常微分方程代考
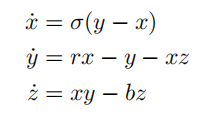
has a FP at the origin for all parameter values, and for r > 1, two new ones appear,
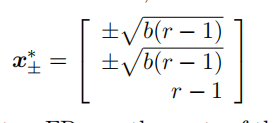
The eigenvalues for each of these two FPs are the roots of the same not-easily-solvable cubic equation 常微分方程代考
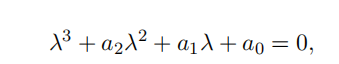
where a2 = σ + b + 1, a1 = b(r + σ), a0 = 2σb(r − 1).
Use a computer code to compute the roots numerically, and plot the real and imaginary parts of each of the three roots as a function of r, for the default values σ = 10 and b = 8/3.
Show that there is a bifurcation at
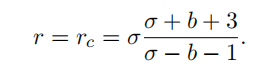
Explain what happens as r exceeds rc. 常微分方程代考
- For σ = 10, b = 8/3 and r = 28, make a Python program to collect just the values of the peaks (local maxima) of z(t), which we’ll call zn, for n = 1 . . . N. Run the code long enough to make sure N is at least in the 100s. Now make a plot of zn+1 vs. zn. You should see a pattern emerge! This is a discrete map that emerges from the continuous system. Skecth a similar function on paper, and try to make a cobweb plot. Convince yourself that there are no periodic orbits.
- A key feature of chaotic system is “sensitive dependence on initial conditions”, meaning infifinitessimal difffferences in the initial conditions will lead to wildly difffferent trajectories.
Here you will demonstrate this numerically. Write a program that computes two trajectories (solutions to the Lorenz system) from two nearby initial conditions, i.e. choose x(0) = x0,
and˜x(0) = x0+ (e.g. just add an arbitrarily small number to any or all of the components of x(0)0). Step the trajectories forward, and at each time, compute the “distance” betweenthem, δ(t) = |x(t) − ˜x(t)|. Chaotic systems have exponential separation of paths, 常微分方程代考
![]()
Plot ln[δ(t)] and estimate the exponent γ. This is a Lyapunov exponent of the system; if it’s positive, there is a time horizon beyond which the system state can no longer be predicted from the initial condition.





发表回复
要发表评论,您必须先登录。