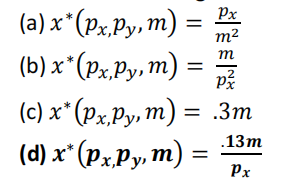
Final Exam – Fall 2014 – Econ 10A
经济final代考 If the annual interest rate increases, what you can you say about the direction of change due to the substitution effect and income
(1) Steven can choose between two goods: consumption in the current period and consumption in a future period. He also has positive income at both time periods. Given the nominal interest rate, the inflation rate, and Steven’s income in each period, he is currently a borrower. If the inflation rate increases, but the nominal interest rate and Steven’s income do not change, which of the following statements is true? Assume that his indifference curves are well-behaved.
(a) He could end up with a higher or lower utility with the new inflation rate 经济final代考
(b) He must end up with a lower utility with the new inflation rate
(c) His new intertemporal budget constraint is a parallel shift from the original intertemporal budget constraint
(d) He will consume nothing in the future with the new inflation rate
(e) He must end up with higher utility
Steven’s utility will increase if Steven consumes at a higher indifference curve and, therefore, a higher budget constraint. To figure out whether his budget constraint expands, we need to figure out the endowment point and the intercept to see how they move as inflation increases. Given that Steven’s endowments in the two period are in monetary terms, his budget constraint is:
(1 + ?)?1 + ?2 = (1 + ?)?1?1 + ?2?2
Then, the endowment point is (?1, ?2) =![]() The horizontal intercept (where consumption next period is 0) is given by ?1 =
The horizontal intercept (where consumption next period is 0) is given by ?1 =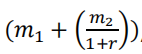 /?1 and the vertical intercept (where consumption current period is 0) is given by ?2 = ((1 + ?)?1 + ?2)/?2.
/?1 and the vertical intercept (where consumption current period is 0) is given by ?2 = ((1 + ?)?1 + ?2)/?2.
Because 1 + ? =![]() Infl ation rate can go up if ?1 decreases or ?2 increases. If ?1 decr eases, the horizontal intercept moves to the right and budget constraint expands. This makes Steven better off. If ?2 increases, the vertical intercept moves down and budget constraint shrinks. This makes Steven worse off.
Infl ation rate can go up if ?1 decreases or ?2 increases. If ?1 decr eases, the horizontal intercept moves to the right and budget constraint expands. This makes Steven better off. If ?2 increases, the vertical intercept moves down and budget constraint shrinks. This makes Steven worse off.
Therefore, it is unclear whether Steven will end up with a higher or lower utility with the new inflation rate.
(2) The max function takes the maximum of two arguments. For example, max(5, 8) = 8. Liv’s utility of two goods x and y is U(x, y) = max(2x, y). Liv currently has an income of 80, the price of good x is currently 10, and the price of good y is currently 4. If the price of good y increases to 8, which of the following statements is true? 经济final代考
(a) The change in the demand for x due to the SE is 0
(b) The change in the demand for x due to the IE is 0
(c) The quantities of both goods demanded stay the same when the price of good y changes
(d) The change in the demand for x due to the SE is positive
(e) The change in the demand for x due to the IE is positive
Due to the curvature of the indifference curves, Liv will always have a corner solution (i.e. will only consume a positive quantity of one of the commodities.)
Initial demand: (0, 20) because U(0, 20) = 20 and U(8, 0) = 16.
New demand after the price change: (8, 0) because U(8, 0) = 16 and U(0, 10) = 10.
Point B: New prices with the same utility as the initial demand: Consume only x due to the new price ratio. U(x, 0) = 20
2x = 20 x = 10. So the SE of x is 10 – 0 = 10, and for y is 0 – 20 = – 20. The income effect is 8 – 10 = – 2 for x and 0 – 0 = 0 for y
(3) Which of the following is NOT a monotonic transformation of U(x1, x2) = 37x2 +68x1 – 89? 经济final代考
(a) f(U(x1, x2)) = (U(x1, x2)) /89
(b) f(U(x1, x2)) = (U(x1, x2)) + 89
(c) f(U(x1, x2)) = (U(x1, x2))89
(d) f(U(x1, x2)) = 89(U(x1, x2))
(e) f(U(x1, x2)) = (U(x1, x2)) – 89(U(x1, x2))
(a)? Yes, because dividing by 89 is a monotonic transformation
(b)? Yes, because adding 89 is a monotonic transformation
(c)? Yes, because taking to an odd power is a monotonic transformation
(d)? Yes, because multiplying by a positive number is a monotonic transformation 经济final代考
(e)? No, because when you simplify you get –88(U(x1, x2)), and multiplying by a negative number is not a monotonic transformation.
4) Boney Bird Bath, Inc., requires only labor to make bird baths. Their production function is ?(?) = √?. What is the average productivity of labor at L = 4?
(a) 0.5
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
(e) None of the above
AP of labor is Q / L = √4 / 4 = ½ = 0.5.
(5) Tony is figuring out costs for a new pizza restaurant he plans on opening. His monthly rent is (1000 + 2X) dollars, with X denoting the number of square feet of the restaurant. His variable cost is (3Q2 / X), with Q denoting the number of pizzas he will sell in a month. What is the short-run marginal cost of making pizzas if the size of Tony’s restaurant is 200 square feet, and he sells 900 pizzas per month? 经济final代考
(a) 16
(b) 20
(c) 24
(d) 27
(e) 30
VC = 3Q2 /200. SRMC is the derivative of VC with respect to Q: 6Q/200 = 3Q/100. At Q = 900, SRMC = 3(900)/100 = 27.
(6) Danny has $100 to spend to make ham sandwiches and nothing else. Each sandwich requires 2 pieces of bread and 8 ounces of ham. Which utility function below best represents Danny’s preferences? Let b denote pieces of bread and h denote ounces of ham.
(a) U(b, h) = min(b/8, h/2)
(b) U(b, h) = min(8b, 4h)
(c) U(b, h) = min(b, h/4)
(d) U(b, h) = min(b/8, 4h)
(e) U(b, h) = min(8b, h/4)
The number of sandwiches is min(b/2, h/8). So find one of the answers above that is a monotonic transformation (c), because 2x min(b/2, h/8) = min(b, h/4).
(7) If the inflation rate is 25% and the real interest rate is 60%, what is the exact nominal interest rate? 经济final代考
(a) –35%
(b) 35%
(c) 45%
(d) 85%
(e) 100%
One of the ways to solve this is to know that (1 + inflation rate) (1 + real interest rate) = 1 + nominal rate (1.25)(1.6) = 1 + nominal nominal = 100%.
(8) Jasmine’s daily utility is the cube root of her consumption in dollars, ?(?) = 3√?. She is an expected utility maximizer. Her consumption for tomorrow will be either $64 or $1000, each with 50% probability. If her consumption tomorrow would instead be $X with certainty so that she has the same utility, what is X?
(a) The cube root of 1049
(b) 49
(c) 343
(d) 532
(e) None of the above
U(64) = 4, and U(1000) = 10. The average of these utilities is 7. We need to ask for what consumption today gives a utility of 7? 3√? = 7 X = 343.
(9) What is the marginal product of labor?
(a) The increase in revenue from increasing labor by one unit, holding capital constant
(b) The increase in revenue from increasing labor and capital by one unit
(c) The increase in output from increasing labor by one unit, holding capital constant
(d) The increase in output from increasing labor and capital by one unit
(e) None of the above 经济final代考
By definition
(10) Which of the following is a valid demand function, based on the scale invariance criterion from lecture?
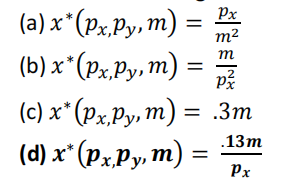
(e) More than one function above is a valid demand function
Recall that F scale invariant iff F(λx1, λx2) = F(x1, x2), for all x1, x2, λ > 0. Only (d) has this characteristic: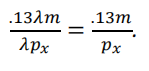
(11) The price of songs (S) is $1 each, and the price of magazines (M) is $8 each. Neal has $160 to spend on these two commodities. His utility function is ?(?, ?) = ? + 3?. If the price of magazines decreases to $4 each, what is the change in the quantity demanded of songs due to the substitution effect? 经济final代考
(a) –160
(b) –40
(c) 0
(d) 20
(e) 40
If the price of songs is less than one-third of the price of magazines, Neal will spend all his income on songs. Thus, when the price of sons is $1 each and the price of magazines is $8 each, Neal will buy 160 songs and no magazines. His utility is 160. When the price of magazines decreases to $4 each, the price of songs is still less than one-third the price of magazines, and Neal will continue to buy 160 songs and no magazines. His utility is still 160. The price increase does not reduce his utility. It has no income effect. Since the total effect is zero, it has no substitution effect, either
(12) Geo’s utility function is described as LeY2 , where Le is hours of leisure per day, and Y is disposable income per day. Geo is employed in a job with a wage of $40 per hour and has 12 hours per day that he can spend in either working or leisure. His income from working is his only source of disposable income. He does not receive any non-wage income. Geo can work as many hours as he chooses, up to the limit of 12 hours per day. How many hours will Geo choose to work at this hourly wage rate? 经济final代考
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 8
(d) 10
(e) 12
MRS = –w ?22??? = ? → ? = 2???. Plug this into the budget constraint: ??? + ? = 12? + ?? → ??? + 2??? = 12? → ?? = 4 → ?? = 12 − 4 = 8.
Please remember to write your name on the front cover, and bubble in your test form on your scantron 经济final代考
Solve each problem in the space provided on that page. Solutions written elsewhere will not be graded
(13) Mark’s intertemporal utility is ?(?1, ?2) = ?1?2, with c1 and c2 denoting consumption today and one year from today, respectively. Mark’s income today is $500 and next year it will be $1650. His annual interest rate is 10%. (There is no inflation in this problem.)
(a) (3 points) What is Mark’s optimal consumption in both time periods?
??? = −(1 + ?) → ?2 ?1= (1 + ?) → ? 2 =(1 + .1)?1.Plug this into the intertemporal budget constraint: 1.1?1 + ?2 = 1.1 × 500+ 1650 = 2200. Solve for c1 to get 1000, and c2 is 1100. 经济final代考
(b) (3 points) If the annual interest rate increases, what you can you say about the direction of change due to the substitution effect and income effect? Assume that Mark continues to be a borrower after the change in the interest rate. You must justify your answer using math, words, and/or a graph to receive any credit. (You do not need to calculate the exact numbers. Only justify the direction of each effect.)
If the interest rate increases, then the slope increases. The higher interest rate makes future consumption relatively more desirable, which leads to a negative SE for consumption today and a positive SE for consumption in the future. To calculate the income effect, note that the cost of borrowing is now higher, which lowers overall purchasing power for a borrower. So the IE is negative for consumption in both time periods. (You can also use a graph to show the SE and IE.)
(14) A firm’s production function is ? = ?(?, ?) = min(√?, ?). The wage rate is 10, the cost of capital is 20, and the price of the good being sold is 200. State your answers below in terms of Q, the quantity produced. 经济final代考
(a) (3 points) If the amount of capital is fixed at 4 units, what is the short run supply that will maximize profits? With capital fixed at 4 units, note that only the first 16 units of labor will have positive marginal productivity. So the following problem needs to be solved, subject to no more than 16 units of labor being used: max? 200√? − 10? − 20?�. Take the first order condition to get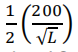 − 10 = 0. Solve for L = 100. Note that this is more than our constraint of 16 units of labor being used at most. So L = 16. (Note that profit is positive here, so there is no need to check the shut-down condition.)
− 10 = 0. Solve for L = 100. Note that this is more than our constraint of 16 units of labor being used at most. So L = 16. (Note that profit is positive here, so there is no need to check the shut-down condition.)
(b) (3 points) What is the long-run supply that will maximize profits? TC is 10L + 20K. To minimize cost for a level of production, L = Q2 and K = Q. So TC = 10Q2 +20Q. So MC = 20Q + 20, and MR = 200. Set MR = MC and solve to get Q = 9. (Again, profit is positive. So there is no need to check the shut-down condition.)
(15) (5 points) Given the production function ? = ?(?,?) = ? + 5?, what is the long-run conditional demand for capital? Express your answer as a function of w, r, p, and ?� .
- If 5w = r, then each technology is equally productive per dollar spent. (One unit of K makes 5 units and costs 5w; five units of L make 5 units and costs 5w.) So if 5w = r, then choose any combination of L and K such that L + 5K =?�.
- If 5w < r, then labor is relatively less expensive: ? = ?� and K = 0.
- If 5w > r, then capital is relatively less expensive: 5? = ?� → ? = ?�5
(16) (5 points) Adam’s daily utility function includes doughnuts (D) and hard-boiled eggs (H): ?(?, ?) = ? + √?. If the price of a doughnut is 2, the price of a hard-boiled egg is 1, and Adam’s daily spending is 15, how many of each commodity will Adam buy each day?
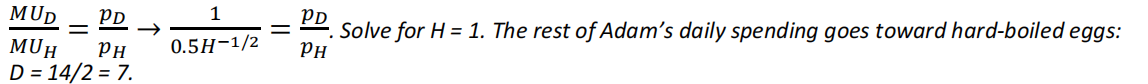

更多代写:cs代写 计量经济代考 机器学习代写 r语言代写 introduction写什么




发表回复
要发表评论,您必须先登录。